The “quality” of leads is more crucial than their amount. That’s why a business usually divides leads into several types, especially if a sales funnel has lots of stages. It often happens in the B2B sphere, e-commerce or niches where customers can for months make a decision to buy the product. Read how to make a step-by-step classification of leads and why is it important to do so.
- 1. Wisely allocate the load on the sales department
- 2. Find out weak points of the sales funnel
- 3. Evaluate the work of an advertisement and optimize campaigns
- 4. “Warming up” leads who are not ready for the purchase yet
- Information Qualified Lead (IQL) or NQL (non-qualified lead)
- MQL (Marketing Qualified Leads)
- SAL (Sales Accepted Leads)
- SQL (Sales Qualified Leads)
Lead is a potential buyer who expressed an initial interest in your product. Moving by a sales funnel he can turn into your customer, however, it is not obvious.
For example, a lead is the one who:
- came from ad to the website and filled in the online request;
- downloaded useful content, leaving his contacts instead;
- registered for a webinar;
- called to specify some information concerning the product;
- agreed on a meeting during a cold call from your sales rep.
The thing is not every lead is actually interested in your product. Only 5-15% of people who are conditionally considered as potential buyers are ready to talk to the sales department. That’s why it is crucial for a company to understand the stage of decision making where a person is right now and whether he is ready to make a purchase. It especially concerns companies that have a lot of touchpoints with customers.
Perfectly, potential customers move by the sales funnel as in the example below. Nevertheless, in reality, part of leads quits at some stages and another part is not even potential customers at all.
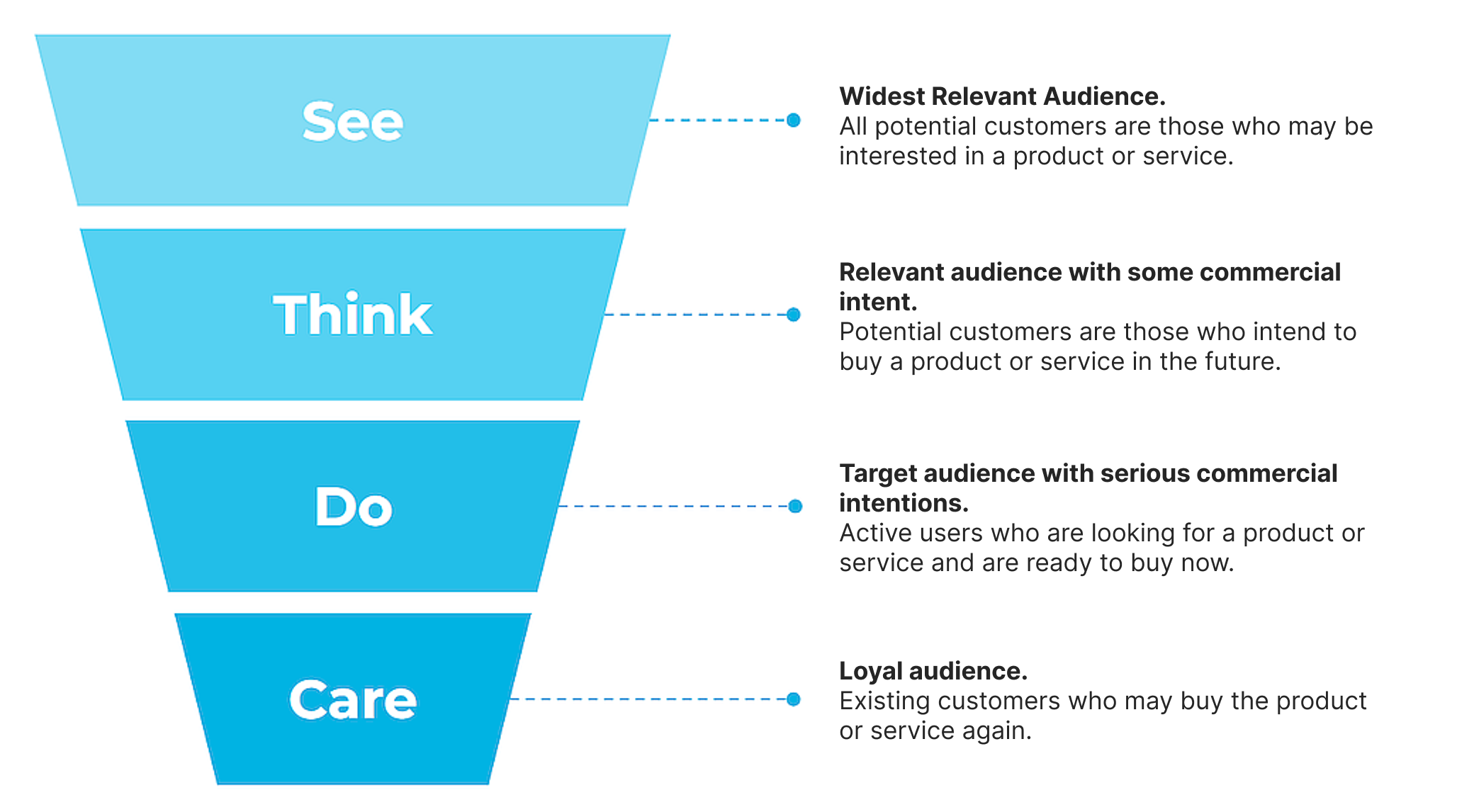
Let’s set an example of the English language courses that have a test for knowledge assessment and e-book “Top 300 useful English expressions for travelers” on the website. It is required to leave the email to receive test results or the book. Language courses could receive emails of four users in a day. At first sight, it may seem that these are leads.
By going deeper it will turn out that:
- user А passed the test as he wanted to discover his level of English to put results at CV;
- user В was going on a vacation abroad and decided to learn the language;
- user С mistakenly thought that by entering an email he will receive a discount for tuition;
- user D is searching for language courses and wanted to view the quality of a test and book.
All in all, we receive only one potential customer — the last visitor. The first two didn’t even think to register for courses and the third one has a limited budget so lessons won’t be available for him without a discount. However, leads like the user D can move by the funnel and sign up for English lessons.
Why leads classification is required
1. Wisely allocate the load on the sales department
By classifying leads you can save your time as well as your sales reps. For example, the sales department can be divided into two parts.
- Employees who provide an introductory consult. They can figure out from leads whether they really need the product, how soon they are planning to make a purchase and whether they have enough budget to do so;
- Sales reps who close deals. In other words, they have negotiations with customers who are ready to buy. They also make offers, go to meetings, etc.
Thus, you can rationally schedule your time. A sales rep knows the type of customer he is talking to and the stage of decision making where he is now. This way, an employee can choose the way of talking to each lead and more likely to push him to the next funnel stage.
2. Find out weak points of the sales funnel
Imagine that a company has the following sales funnel:
- transfer from the advertisement;
- call or request to the chat;
- registration for a consult;
- consultation or demonstration of the service;
- sales.
There are potential customers in each of these stages. Their classification, depending on a stage, will be discussed below. Let’s say we see that 100 people were driven by an advertisement. 70 out of them called, however, only 5 registered for a consult.
This is a reason to sets off alarm bells. The thing may be in sales reps if a product and price are competitive. For example, they don’t handle objections, miss calls or confused with the product. Thus, there are transfers and requests but almost none registres for a consult.
Another situation may be there as well. There are calls but from people who are about to buy a different product. It means that the ad may be launched in the wrong way. For example, the description that is too abstract, incorrect keywords or creatives that confuse users.
Call tracking helps to reveal both these difficulties. It is possible to listen to calls in its interface. Keywords that bring customers are also displayed there. By comparing this data, it becomes clear why random people come from ads but not leads. And who is responsible for low sales — marketing or sales reps.
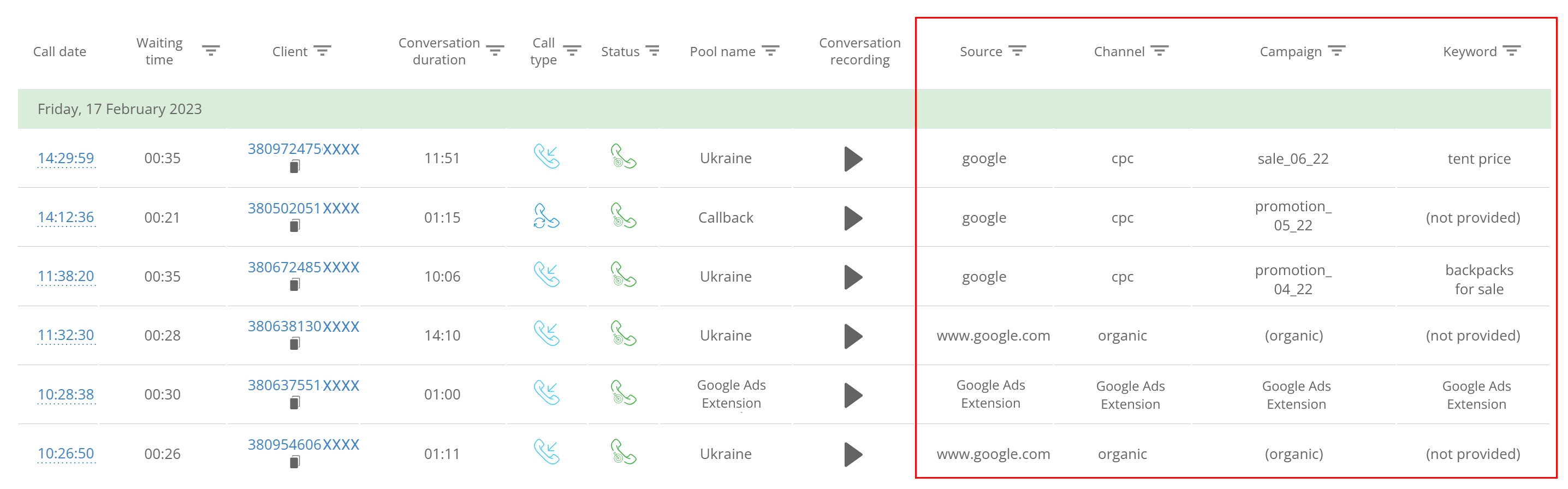
3. Evaluate the work of an advertisement and optimize campaigns
The classification of potential buyers is highly important for marketing. It helps to see the “quality” of leads that come from definite channels. And whether they, all in all, transform into customers.
If you have several campaigns launched — it is possible to discover the most effective one. Let’s say a lot of leads were brought from the display ads but only 3% of them reached the consulting stage. Search paid ads drove fewer potential buyers, nevertheless, they are more “qualified”. 30% of them achieved the reservation.
Having this information, you can allocate the budget in another way. Invest more in paid ads and invest less in the display ads. It is also likely to analyze recordings of calls and what say customers who came from this campaign. Thus, you will understand what is wrong with the advertising message. And will be able to change it.

That’s why it is not likely to instantly get rid of channels that don’t bring sales from your point of view. Firstly, create a hypothesis, invest more in the channel that seems effective. And then, evaluate the result in the whole perspective”
4. “Warming up” leads who are not ready for the purchase yet
You must admit that there is no sense to call a person and sell the product if he subscribed to the newsletter only. This is more likely to scare. But even those who are on the top of the funnel can be slowly ingratiated to the brand and moved further by the sales funnel. Therefore, each type of leads needs to be addressed in a different way.
To do so, you need to understand on which stage of decision making the user is placed right now. Consequently, offer him the relevant content. For example, Ringostat is sending absolutely different emails for:
- blog subscribers;
- users that started a free trial;
- partners, etc.

Leads classification
There is no common classification of leads. It may be highly different for various companies due to the peculiarities of business. How to evaluate potential customers — marketing and sales department decide this together. They develop a system of leads rank. A company may even assign them marks according to their preparedness to buy.
We will start with the most popular system. Even those who are not related to marketing and sales have heard about them. This is the division of leads by their “warmness”.
- Cold. A customer is not ready to make a purchase, he might even not knowing about your company. Sales reps work with such an audience while making cold calls.
- Warm. Lead already knows about the company and you may have an introductory contact with him. He is not ready to buy right now but in general, he is loyal.
- Hot. A customer is ready to make a purchase. You only need to discuss some details and the deal can be closed.

Source: https://marketingforadvisers.co.nz
Another classification is used more often among marketers. Stay tuned — we will describe it below.
Information Qualified Lead (IQL) or NQL (non-qualified lead)
A lead who left the information on him in return for useful data: white paper, investigation, free lesson. It’s the top of a funnel and such a user possibly doesn’t even need your product. He can be moved on the next stage via:
- invite on a free webinar;
- cases;
- free examples of the product;
- catalogs.

Roulette on the website of Neil Patel. By entering his email, a user can receive effective content.
MQL (Marketing Qualified Leads)
Inbound leads that came from channels for which marketing is responsible. For example, from paid ads, organic search, provided events, social media, etc. Such leads are transferred by the marketing department to the sales one so they will be classified there. The more users like that go to the next stage — the higher is the rate of marketing department effectiveness.
The customer journey does not necessarily start with an advertisement or a cold call. Word-of-mouth, a recommendation of acquaintances or loyalty program “Bring a friend”, all this can also drive leads.
SAL (Sales Accepted Leads)
This is MQL that was considered as a potential customer. For example, sales reps talked to him for once and made sure that he needs a product. Or he was the first to write and asked for the contact information of a sales rep. If it is discovered that such a lead is not ready to buy, his contacts are returned back to the marketing department. Sometime after, they can warm him up via content and SAL will transform to SQL.
SQL (Sales Qualified Leads)
A lead that was classified as a potential customer by the sales department. For example, he really has a need for the product, he is a person who makes the decision, etc. The sales department actively works with such a customer, trying to close the deal.

The “Demand Waterfall” model that shows the transfer of a random visitor to a customer
Example of leads classification
As was said before the classification of leads may be totally different, depending on the company. Let’s set the example of Ringostat and see how this process can be provided with SaaS.
- A visitor is driven to the website from ads and made a proper action. For example, he calls, texts the chat or blog, downloads content. Thus, he becomes MQL.
- Clients’ contacts are given to SDR (Sales Development Representative). Their task is to talk with a client and understand whether he really has a need for our product, whether it is possible to contact him, whether it’s not spam. Information on the lead is entered into the CRM.
- If this client is a potential one, he becomes SQL. Sometimes it happens that it is impossible to call the user, he tries himself to sell something or he came from not relevant request. In such a case a deal is marked as lost in the CRM. The reason for it is also mentioned there. If it becomes clear that an advertisement drives junk leads only, marketers find out the reason for it and optimize campaigns.
- Specialists show a demo for the client on the next stage. It is done by AE — Account executive. They also connect a free trial and close the deal. This process allows not involving them initially until SDR won’t make sure that they are talking to a potential client.
How to build the process of leads classification
1. First of all, analyze the sales funnel and note yourself in detail the behavior of a potential buyer on each of its stages, as well as the building of the work of your sales department. This will help to understand whether you will have SAL or SQL only, whether there is a sense to classify leads as cold and hot.
2. Create an ICP (Ideal Customer Profile). Remember that in B2B it is rather an organization than a person. The budget, the position that occupies the person responsible for decisions, the number of employees, etc. Analyze the best clients, possibly, they have common features that are better to be included in the profile.
3. Create a separate table and enter characteristics of the “ideal customer”. Leave a question for sales reps, in front of each of them. Asking them while talking to leads they will be able to define who is a potential client and who is not. For example, it is barely possible that an unemployed young mother will become a customer of a company that sells industrial refrigeration equipment. It is also useful to ask questions from so-called BANT concept:
- B (Budget) — whether a client is ready to pay for your product;
- A (Authority) — whether the person you are talking to is the one who makes the final decision;
- N (Need) — the most important metric: whether the client really needs your product;
- T (Time frame) — whether a purchase is planned for right now or for a perspective.
4. Some companies also use the scoring of leads. It allows evaluating the priority of work with the client. For example, the number of products that the client is going to buy, his budget for the promotion — if you are an agency, etc. This affects the score that is assigned to the lead.
5. After a conversation with the potential client, a sales rep enters answers on questions to the CRM. It is better to customize the workspace there that will correspond to the funnel stages. If clients often call you it is comfy when data on calls are automatically transferred to the CRM.
Conclusions
1. Not all users who interact with a brand become customers, as a result. That’s why a business has to classify leads by their readiness for the deal.
2. By classifying leads, a company can:
- rationally distribute the workload on the sales department — firstly, it is better to discover the client’s needs, his opportunities, and only then transfer him to the demo demonstration, negotiations, etc.;
- find out weak points of the sales funnel — the stage when they “quit” it and why;
- evaluate how works the advertisement — and which channels bring customers that make a purchase, all in all;
- “warm-up” leads that are not ready to buy yet — create unique content for each class.
3. There are different systems of leads classification. The most popular is division on “hot”, “warm”, “cold”, as well as MQL, SQL. In other words, classified by marketing or sales.
4. It is required to analyze the sales funnel to make the classification system. Thus, you will understand the type of leads that are presented for a specific business model. After this, you need to create a profile of an ideal customer. The questionnaire is made on its basis and then sales reps use it while talking to customers. It helps to discover whether a client needs the product and how soon, whether his budget is enough, etc.
5. After the conversation with a lead, the sales rep enters information on him to the CRM. Potential buyers that are not ready yet, are transferred back to the marketing department so they will be “warming them up”. It is possible to use newsletters, social media, useful content and remarketing to do so.